Installing and Running Graphite via RPM and Supervisord
When you are running distributed applications such as Hadoop or Storm a key success factor is gaining meaningful operational insights into what’s happening in your cluster environments.
Graphite is popular backend tool to collect system and application metrics that will help you achieve that level of understanding – be it during development or for running your applications in production. To get you started with metrics collection via Graphite I have documented the instructions for a basic setup of Graphite. As a bonus we will build our own RPMs to create the foundation for automated deployments of this Graphite setup via tools like Puppet and Chef.
- What we want to do
- Versions
- Building RPMs for Graphite 0.9.10
- Installing prerequisites
- Installing Graphite
- Starting Graphite
- Where to go from here
What we want to do
We will install and configure Graphite 0.9.x via RPMs on RHEL 6 and run it under process supervision with supervisord.
In further detail:
- We will build RPM files for Graphite (which does not provide any offically). This allows a smooth transition to a config management tool such as Puppet or Chef to automate deployments.
- We will use gunicorn to run
graphite-web, Graphite’s web frontend. By default it will listen on http://localhost:8080/ after installation. - We rely on supervisord to run – and start/stop – the Graphite-related daemons
gunicornandcarbon-cache(the latter daemon collects the actual stats data from other applications).
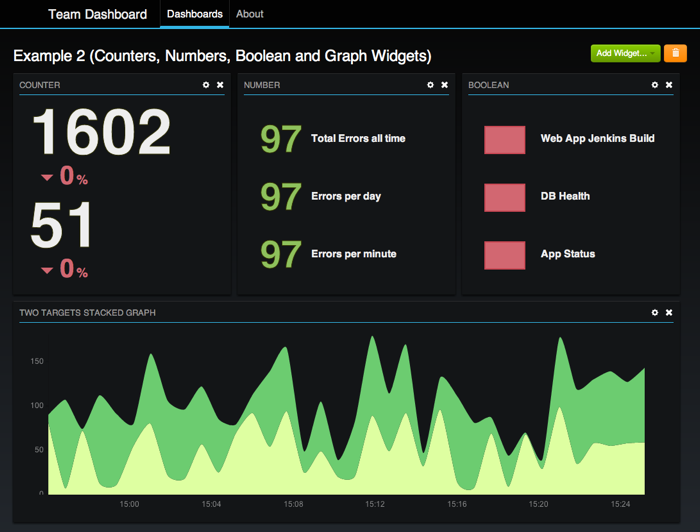
Once installed you can collect metrics from your applications and infrastructure tools, and add visually appealing dashboards on top of Graphite to add (meaningful) lipstick to Graphite’s default web frontend:
Versions
The instructions below are based on and have been tested with the following software versions:
- OS: RHEL 6 / CentOS 6
- Graphite 0.9.10
Building RPMs for Graphite 0.9.10
We are using fpm to build our own RPMs for Graphite.
carbon
Graphite is comprised of two components, the webapp frontend graphite-web, and the backend storage application
carbon. Data collection agents connect to carbon and send their data,
and carbon’s job is to make that data available for real-time graphing immediately and try to get it stored on disk as
fast as possible.
$ fpm -s python -t rpm \
-d python-setuptools \
-d Django -d django-tagging \
-d python-devel \
-d python-twisted \
-d python-memcached \
-d python-sqlite2 \
-d bitmap -d bitmap-console-fonts -d bitmap-fixed-fonts -d bitmap-fonts-compat \
-d bitmap-lucida-typewriter-fonts -d bitmap-miscfixed-fonts \
-d pycairo \
carbon
# this will create => python-carbon-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm
whisper
Whisper is a fixed-size database, similar in design to RRD
(round-robin-database). It provides fast, reliable storage of numeric data over time. It is used by the carbon
storage backend.
$ fpm -s python -t rpm \
-d python-setuptools \
-d Django -d django-tagging \
-d python-devel \
-d python-twisted \
-d python-memcached \
-d python-sqlite2 \
-d bitmap -d bitmap-console-fonts -d bitmap-fixed-fonts -d bitmap-fonts-compat \
-d bitmap-lucida-typewriter-fonts -d bitmap-miscfixed-fonts \
-d pycairo \
whisper
# this will create => python-whisper-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm
graphite-web
graphite-web is the web frontend of Graphite, based on Django.
$ fpm -s python -t rpm \
-d python-setuptools \
-d Django -d django-tagging \
-d python-devel \
-d python-twisted \
-d python-memcached \
-d python-sqlite2 \
-d bitmap -d bitmap-console-fonts -d bitmap-fixed-fonts -d bitmap-fonts-compat \
-d bitmap-lucida-typewriter-fonts -d bitmap-miscfixed-fonts \
-d pycairo \
-d python-gunicorn \
graphite-web
# this will create => python-graphite-web-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm
Optional: carbon-cache init script
This step is only needed if you do not want to run carbon-cache via supervisord.
If you do not want to run carbon-cache via supervisord follow the instructions below to create an RPM that
bundles a simple carbon-cache init script.
$ sudo cp init-scripts/carbon-cache /etc/init.d
$ fpm -s dir -t rpm -a all -n carbon-cache-init-script -v 1.0 /etc/init.d/carbon-cache
$ sudo rm /etc/init.d/carbon-cache
# this will create => carbon-cache-init-script-1.0-1.noarch.rpm
After this RPM is installed you can start/stop carbon-cache via /etc/init.d/carbon-cache.
Installing prerequisites
We will use supervisord to run the various Graphite daemons.
# 'supervisor' is available from EPEL; run fhe following command if you haven't set up EPEL on your machine yet
# $ sudo rpm -Uhv https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
$ sudo yum install supervisor
$ sudo chkconfig supervisord on
# Recommended: secure supervisord configuration file (may contain user credentials)
$ sudo chmod 600 /etc/supervisord.conf
Installing Graphite
Install our custom Graphite RPM files
$ sudo yum install python-carbon-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm \
python-whisper-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm \
python-graphite-web-0.9.10-1.noarch.rpm
By using yum instead of rpm to install the RPM files we can automatically resolve (download and install) the
dependencies of our Graphite RPM files.
Configure Graphite
Define a SECRET_KEY for Django/Graphite
Edit /opt/graphite/webapp/graphite/app_settings.py and set SECRET_KEY to a difficult to guess (random) string.
# Make this unique, and do not share it with anybody.
SECRET_KEY = 'replace-me-with-a-difficult-to-guess-random-and-long-string'
Set up the database used by Django/Graphite
The default backend of Graphite is SQLite. We will stick to that for the time being.
Run the following command to sync the database setup of Django:
# See https://answers.launchpad.net/graphite/+question/187148
$ sudo python webapp/graphite/manage.py syncdb
<snip>
You just installed Django's auth system, which means you don't have any superusers defined.
Would you like to create one now? (yes/no): yes
Username (Leave blank to use 'root'): jsmith
E-mail address: jsmith@example.com
Password:
Password (again):
Superuser created successfully.
Installing custom SQL ...
Installing indexes ...
No fixtures found.
Add a system account for Graphite
We will use a dedicated user account to run the various Graphite daemons. This improves security.
$ sudo groupadd -g 53012 graphite
$ sudo useradd -u 53012 -g 53012 -d /opt/graphite -s /bin/bash graphite -c "Graphite service account"
$ sudo chage -I -1 -E -1 -m -1 -M -1 -W -1 -E -1 graphite
Configure ownership of graphite-web storage directory
$ sudo chown -R graphite:graphite /opt/graphite/storage
Configure graphite-web
Copy local_settings.py
to /opt/graphite/webapp/graphite/local_settings.py:
# When graphite is installed on the same machine as the checkout of this repository
$ sudo cp configs/local_settings.py /opt/graphite/webapp/graphite/local_settings.py
Set up directories and permissions:
$ sudo mkdir /var/run/gunicorn-graphite
$ sudo chown -R graphite:graphite /var/run/gunicorn-graphite
$ sudo mkdir /var/log/gunicorn-graphite
$ sudo chown -R graphite:graphite /var/log/gunicorn-graphite
Add gunicorn to supervisord:
[program:graphite-gunicorn]
command=gunicorn_django --bind=127.0.0.1:8080 --log-file=/var/log/gunicorn-graphite/gunicorn.log --preload --pythonpath=/opt/graphite/webapp/graphite --settings=settings --workers=3 --pid=/var/run/gunicorn-graphite/gunicorn-graphite.pid
directory=/opt/graphite
user=graphite
autostart=True
autorestart=True
log_stdout=true
log_stderr=true
logfile=/var/log/gunicorn-graphite/gunicorn.out
logfile_maxbytes=20MB
logfile_backups=10
If you run into startup problems with gunicorn then increase the log level to see what is failing exactly:
$ gunicorn_django --debug --log-level=debug ...
Configure carbon-cache
Configure the carbon-cache daemon. See also Configuring carbon.
$ sudo cp /opt/graphite/conf/storage-schemas.conf.example /opt/graphite/conf/storage-schemas.conf
$ sudo cp /opt/graphite/conf/storage-aggregation.conf.example /opt/graphite/conf/storage-aggregation.conf
Copy the carbon.conf to
/opt/graphite/conf/carbon.conf:
# When graphite is installed on the same machine as the checkout of this repository
$ sudo cp configs/carbon.conf /opt/graphite/conf/carbon.conf
Set up directories and permissions:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/log/carbon
$ sudo chown -R graphite:graphite /var/log/carbon
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/run/carbon
$ sudo chown -R graphite:graphite /var/run/carbon
Add carbon-cache to supervisord:
[program:graphite-carbon-cache]
; '--debug' is REQUIRED to get carbon to start in a manner that supervisord understands
; 'env PYTHONPATH=...' is REQUIRED because just using the 'environment' option apparently does not work
command=env PYTHONPATH=/opt/graphite/lib carbon-cache.py --config /opt/graphite/conf/carbon.conf --pidfile=/var/run/carbon/carbon.pid --debug start
directory=/opt/graphite
environment=GRAPHITE_ROOT=/opt/graphite,GRAPHITE_CONF_DIR=/opt/graphite/conf,PYTHONPATH=/opt/graphite/lib
user=graphite
autostart=True
autorestart=True
log_stdout=true
log_stderr=true
logfile=/var/log/carbon/carbon.out
logfile_maxbytes=20MB
logfile_backups=5
If you run into startup problems with carbon-cache then increase the log level to see what is failing exactly:
$ carbon-cache.py --log-level=debug ...
Starting Graphite
Start Graphite daemons
Run the following command to start both gunicorn (and thus graphite-web) and carbon-cache:
$ sudo service supervisord restart
Check via supervisorctl whether the daemons are properly running:
$ sudo supervisorctl status
graphite-carbon-cache RUNNING pid 22058, uptime 0:00:10
graphite-gunicorn RUNNING pid 22057, uptime 0:00:10
You can also verify correct startup by inspecting the log files at /var/log/carbon/ and
/var/log/gunicorn-graphite/.
Now you are ready to send metrics to Graphite from your applications.
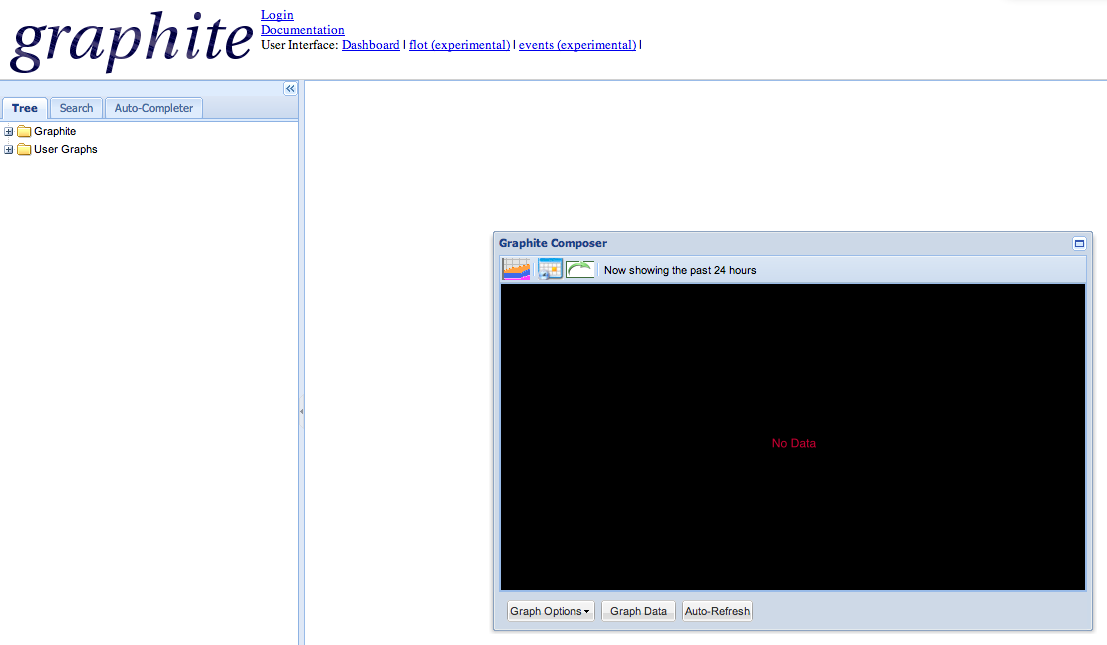
Open Graphite’s web interface at http://localhost:8080/ in your browser and take a look around.
Where to go from here
As mentioned at the beginning of this article the latest version of these setup instructions for Graphite is always available at https://github.com/miguno/graphite-supervisord-rpm.
Add metrics support to your Storm cluster
If you have followed my tutorial Running a Multi-Node Storm Cluster, you can now read the next article and start sending metrics from Storm to Graphite.
Add metrics support to your applications
Graphite is widely supported, for instance by Yammer’s excellent Metrics library, so you should be seeing your own metrics flowing into Graphite very quickly.
I will not go into detail here – finding the right client for your favorite programming language or application is just a web search away. A first starting point is Tools That Work With Graphite.
Add dashboards to Graphite
There are many dashboards available for Graphite. In no order of priority some of the more popular ones are:
- Tasseo – live dashboard for Graphite
- Descartes – introspective dashboard for Graphite
- Graphene – realtime dashboard & graphing toolkit
- Graphiti – front-end and graph storage application for Graphite
- Team Dashboard – visualize your team’s metrics all in one place
The blog post Dashboards for Graphite provides a good overview and comparison between the various options.
Also, I have also compiled instructions on how to install and configure Graphite-Tattle, a self-service alerting and dashboard frontend for Graphite and Ganglia.